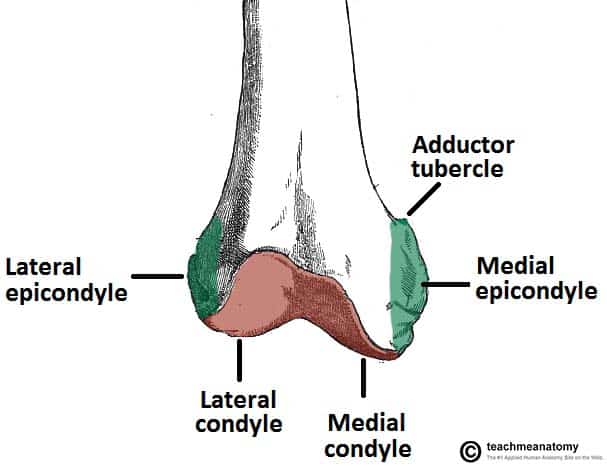
Intercondylar fossa A depression found on the posterior surface of the femur it lies in between the two condyles. As such the vertical ligament found along the inside of the knee that attaches to this bony protrusion of the femur is known as the medial collateral ligament MCL.
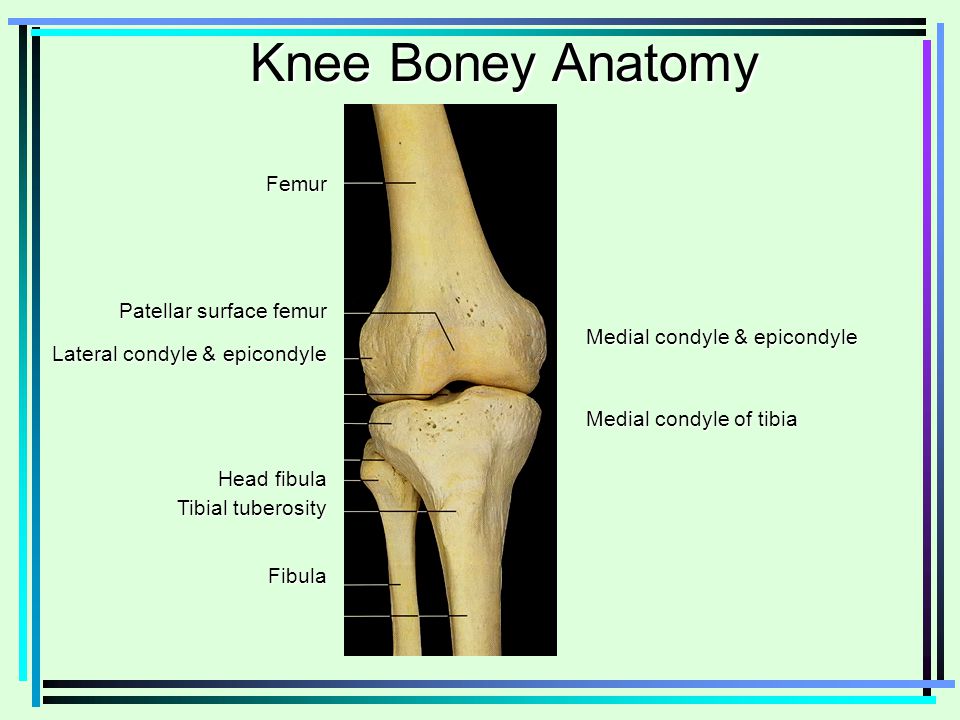
The medial and lateral condyle of the tibia are shown in figure 1.

. 48 The distal iliotibial band has an associated proximal bony ridge which lays 536 mm proximal from the lateral epicondyle and a distal ridge 314 mm proximal from the lateral epicondyle. Which bone does not. Tibia refers to the shin bone.
Apex of the patella b. On the femur the lateral femoral epicondyle sits 236 233 mm proximal from the joint line. Directly below it is a small depression from which a smooth well-marked groove curves obliquely upward and backward to the posterior extremity of the condyle.
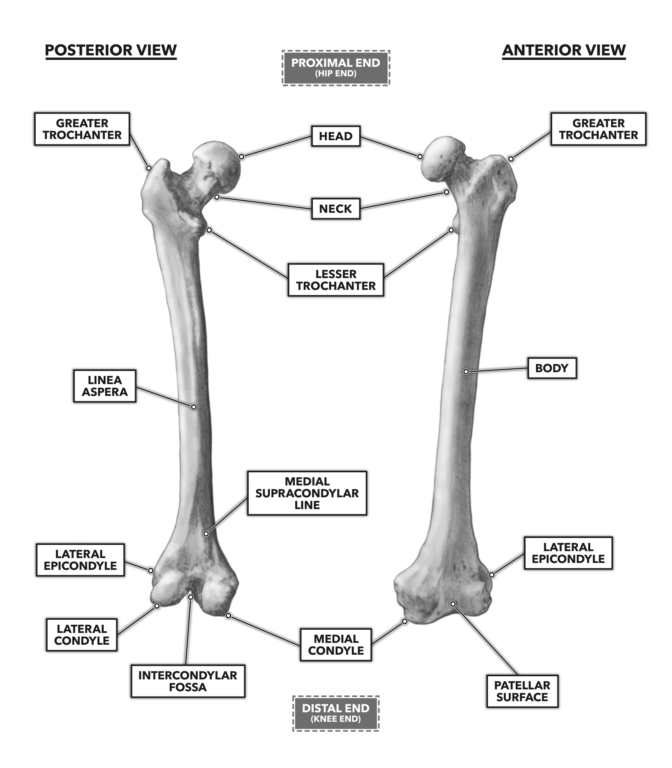
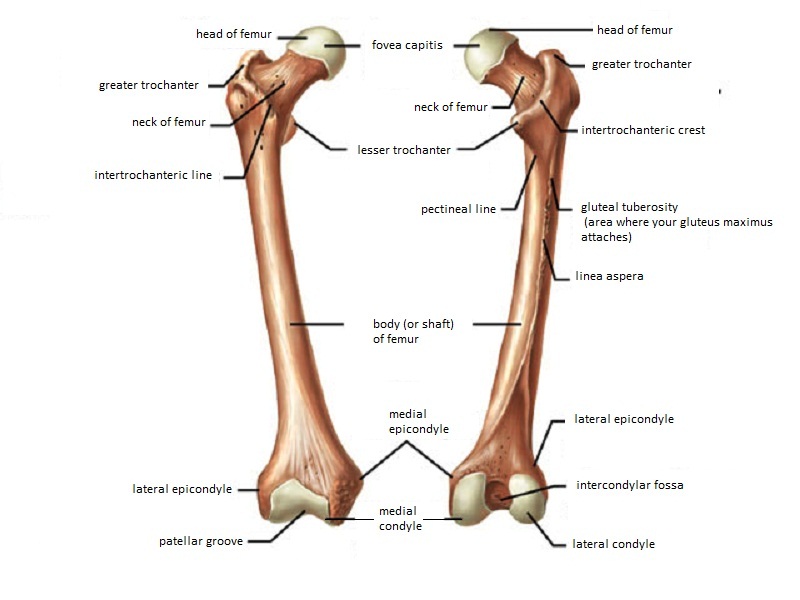
Know the Head of the Femur and that it attaches to the hip joint called the Acetabulum. Located above the medial condyle it bears an elevation the adductor tubercle which serves for the attachment of the superficial part or tendinous insertion of the adductor magnus. The medial and lateral condyles of the tibia articulate with the a.
The lateral epicondyle of the femur smaller and less prominent than the medial epicondyle gives attachment to the fibular collateral ligament of the knee-joint. The medial epicondyle is the larger. It is both the longest and the strongest bone in the human body extending from the hip to.
Lateral Medial Epicondyles Femur detailed with Head of the Femur Greater Lesser Trochanter Medial Lateral Epicondyles Single view of the Femur Bone Hip joint with Femur connection to hip joint Share. This is the spherical flooring which surrounds any joint throughout the bone it is essentially the most distinguished half and is generally thought-about a part of the joint and has distinct. 49 50 On the tibia Gerdys tubercle is located 171 mm.
Medial and lateral epicondyles bony elevations on the non-articular areas of the condyles. Medial in anatomy means toward the midline of the body as opposed to lateral or toward the sides of the body. Etiology Isolated epicondyle fractures are usually caused by avulsion injury to collateral ligaments.
The common flexor tendon and UCL provide stability to flexion and valgus forces at the elbow. The lateral epicondyle of the femur smaller and less prominent than the medial epicondyle gives attachment to the fibular collateral ligament of the knee-joint. The medial epicondyle also serves at the origin of the ulnar or medial collateral ligament UCL.
The medial and lateral condyles are found on the distal end of the femur and those articulate with the knee joint. Head of the fibula e. The medial epicondyle of the femur is an epicondyle a bony protrusion located on the medial side of the femur at its distal end.
Greater and lesser trochanters of the femur. The mandibular condyle is found on the mandible which articulates with the mandibular joint. This tendinous part here forms an intermuscular septum which forms.
It also contains both medial and lateral condyles. They are the area of attachment of some muscles and the collateral ligaments of the knee joint. Medial and lateral condyle.
The lateral epicondyle of the femur smaller and less prominent than the medial epicondyle gives attachment to the fibular collateral ligament of the knee-joint. For nondisplaced or minimally displaced medial epicondyle fractures nonoperative management is the procedure of choice. Medial epicondyle of the humerus lateral epicondyle of the humerus Medial epicondyle of the femur and Lateral epicondyle of the femur.
The medial epicondyle is the common origin of the forearm flexor and pronator muscles. Directly below it is a small depression from which a smooth well-marked groove curves obliquely upward and backward to the posterior extr. Lateral condyle is broader than medial condyle of the femur.
The sMCL femoral attachment is not on the medial epicondyle. The medial and lateral collateral ligaments of the knee originate from their respective epicondyles. On the femur two types of condyles occur in the knee joint.
They usually form part of a more complex fracture around the femoral component. The Femur has a Greater Lessor Trochanter. They are separated by the deep intercondylar fossa proximally bounded by the horizontal intercondylar line.
These fractures are classified by UCPF as V3-A. Medial and lateral condyles of the femur c. Medial and lateral epicondyles of the femur d.
Intercondylar fossa a deep notch on the posterior surface of the femur between the two condyles. In between the medial and lateral femoral condyles is the intercondylar fossa. The femur is the only bone located within the human thigh.
Medial and lateral epicondyles Bony elevations on the non-articular areas of the condyles. Learn more about the femur in this anatomy tutorial. Clinical signs Knee instability Pain Swollen Imaging.
The adductor tubercle can be found slightly distal to the attachment of the adductor magnus tendon and then the medial epicondyle can be found 126 mm distal and 83 mm. Articular surface for medial sesamoid Medial epicondyle Translations Description The medial and lateral condyles form the proximal part of the body of femur and articulate with the proximal part of tibia to form the femorotibial joint. How is a medial epicondyle fracture treated.
Medial condyle is much larger and bears more weight. Isolated medial or lateral epicondyle fractures are rare. The femoral attachment of the sMCL is found by first finding the distal attachment of the adductor magnus tendon.
On each condyle is a smaller epicondyle which serve as the point of attachment for the collateral ligaments the medial collateral MCL and the lateral collateral ligaments LCL. The medial femoral condyles are also distinguished by another anatomical term of location. More controversy exists with displacement of 5-15 mm.
The medial condyle is one of the two projections on the lower extremity of femur the other being the lateral condyle. What muscles originate at the medial epicondyle. There are two condyles found on the proximal end of the tibia and those are known as the medial and lateral condyles of tibia.
Treatment indications Nondisplaced medial condyle fractures can be treated without surgery. The medial condyle is larger than the lateral outer condyle due to more weight bearing caused by the centre of mass being medial to the knee. Directly below it is a small depression from which a smooth well-marked groove curves obliquely upward and backward to the posterior extremity of the condyle.
The Femur Proximal Distal Shaft Teachmeanatomy

Femur An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Knee Boney Anatomy Femur Medial Condyle Epicondyle Ppt Video Online Download
Orif Lag Screw For Lateral Medial Femoral Epicondyle Fracture

Oslo Pilates Og Yoga Her Har Du Larbeinet Ditt Det Taler En Stoyt Noen Tonn For Det Brekker Femur The Femur Is The Only Bone Of The Human Thigh It

0 comments
Post a Comment